Understanding AFib & Stroke Risk

What Is Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) and How Is It Related to Stroke?
What Is AFib?
AFib is the most common type of irregular heartbeat that often causes the heart to beat too quickly.1
How Can AFib Lead to Stroke?
During a normal heartbeat, the upper chambers (atria) and lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart work together to pump blood to the rest of the body. AFib occurs when the upper chambers of the heart beat irregularly and do not pump all of the blood to the lower chambers, causing some blood to pool and potentially form clots. If a clot breaks loose, it can travel through the bloodstream to the brain and lead to a stroke.1,2
How many people in the United States will have AFib?
About 12 million people will have AFib by 2030.5
The risk for AFib increases with age.1
Common Symptoms and Causes of AFib
Some people with AFib do not know they have it because they have no symptoms. Others may experience one or more of the following1:
- Irregular heartbeat: heart racing or skipping beats
- Heart palpitations: fast, fluttering, or pounding
- Feeling lightheaded: dizzy or faint
- Extreme fatigue: feeling tired or sluggish all the time
- Shortness of breath: a tightness in your chest or difficulty breathing
- Chest pain: a dull ache or sharp stabbing pain in your chest
Symptoms can be representative of many conditions. Only a health care provider can determine whether these symptoms indicate AFib or another condition.
The risk of AFib increases with age, and high blood pressure occurs in about 1 in 5 cases of AFib.6 There are some risk factors that may increase your chances of developing AFib. These include but are not limited to1,7:
- Being age 65 and older
- Female sex
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Sleep apnea
- Heavy alcohol use
- Heart disease
- Prior heart attacks and strokes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Overactive thyroid
- Chronic kidney disease
How AFib may lead to a stroke in the brain
During a normal heartbeat, the upper chambers (atria) and lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart work together to pump blood to the rest of the body.1,2
AFib occurs when the upper chambers of the heart beat irregularly, and do not pump all of the blood to the lower chambers, causing some blood to pool and potentially form clots.1,2
If a clot breaks loose, it can travel through the bloodstream to the brain and lead to a stroke.1,2

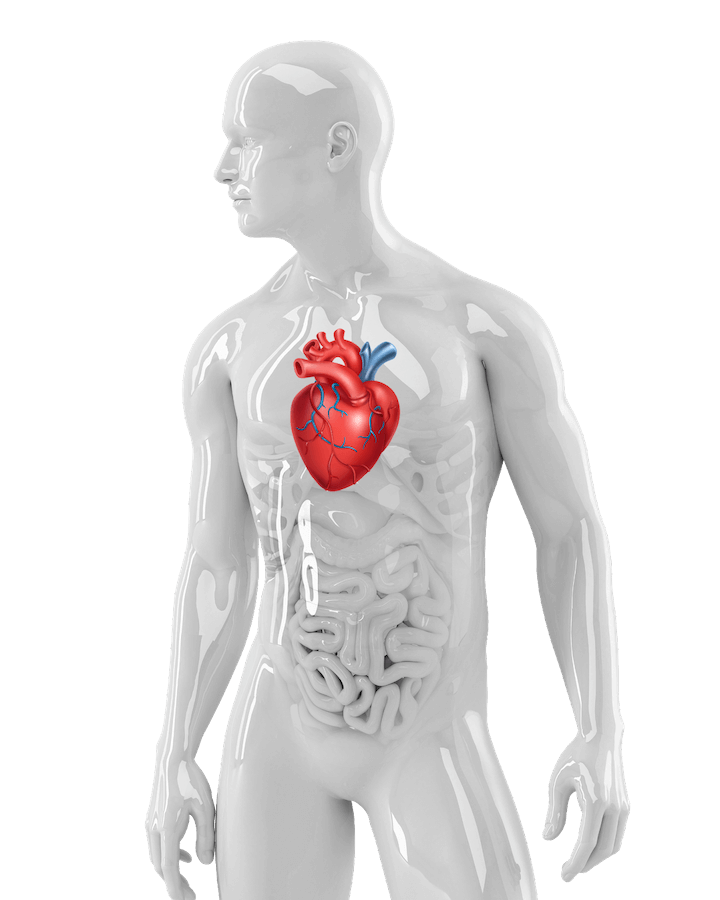
1 A blood clot can form in the heart from AFib and break loose

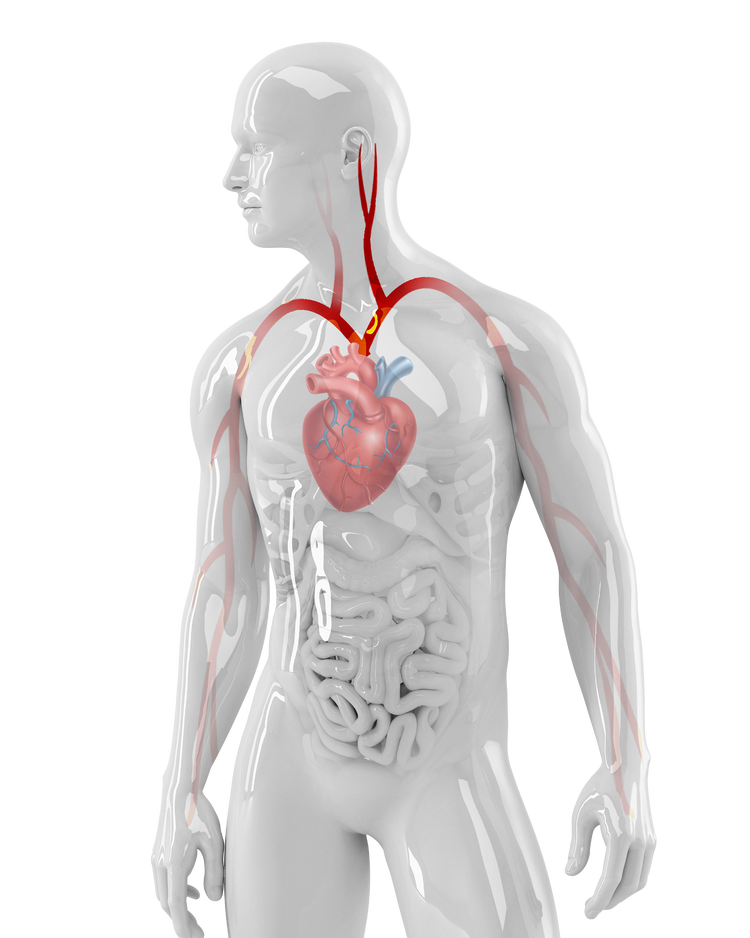
2 Blood clot travels through the bloodstream toward the brain

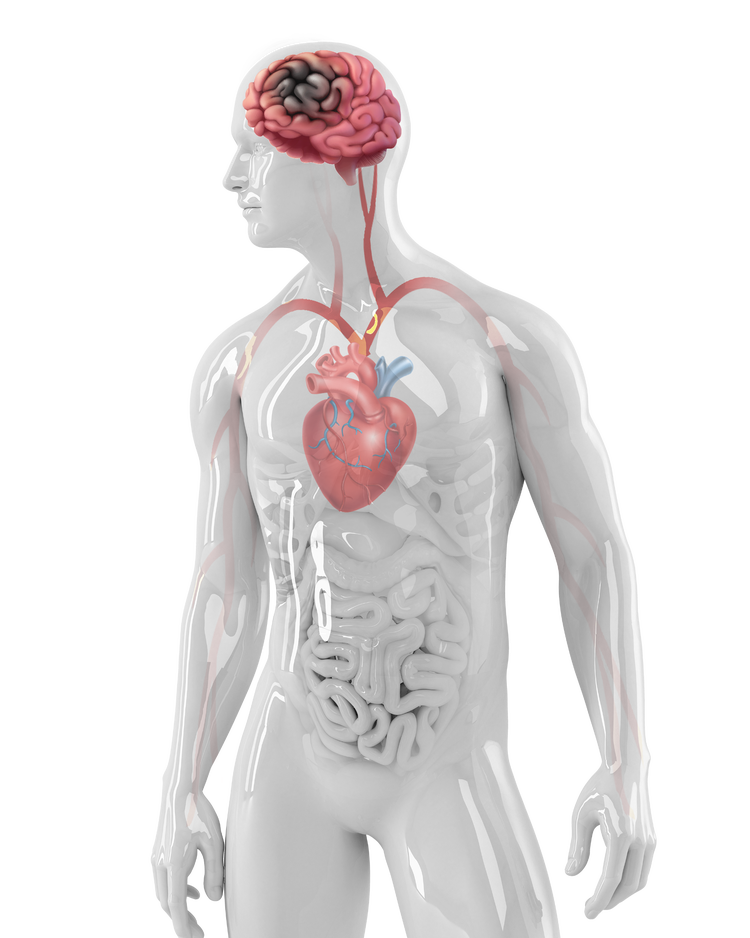
3 Blood clot blocks an artery in the brain, causing a stroke


- Atrial fibrillation: what is atrial fibrillation? Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated October 14, 2022. Accessed May 24, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/atrial_fibrillation.htm
- What is atrial fibrillation? National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Updated November 30, 2022. Accessed May 24, 2023. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/atrial-fibrillation
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22(8):983-988. doi:10.1161/01.STR.22.8.983
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(21):e1-e76. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.022
- Colilla S, Crow A, Petkun W, Singer DE, Simon T, Liu X. Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(8):1142-1147. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.05.063
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56-e528. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659
- Atrial fibrillation: causes and risk factors. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Updated November 30, 2022. Accessed May 24, 2023. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/atrial-fibrillation/causes
- Treat and recover from stroke. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed May 24, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/treatments.htm
- Stroke signs and symptoms. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed May 24, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/signs_symptoms.htm


